Cancer is a disease where some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other body parts. Normally, cells grow and divide to form new cells as the body needs them. When cells grow old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their place. However, in cancer, this orderly process breaks down. Abnormal or damaged cells survive when they shouldn’t, and new cells form when they are not needed. These extra cells can divide without stopping and may form lumps called tumours.
There are many types of cancer, such as breast cancer, lung cancer, and skin cancer. Some cancers form solid tumours, while others, like leukaemia, do not. Cancer can be caused by genetic factors, lifestyle choices (like smoking or poor diet), certain infections, and environmental exposures (like radiation).
Symptoms of cancer vary depending on the type, but they may include lumps, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and skin changes. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of recovery. Blood tests to detect cancer can aid in early diagnosis. Treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy.
According to the World Health Organization, cancer was the top cause of death worldwide in 2020, accounting for about 10 million fatalities. In this blog, we will discuss cancer in detail, including symptoms, types, causes, and Treatments.
What is Cancer?
Cancer disease is a life-threatening condition in which your cells begin to develop in an unregulated manner. Uncontrolled development and proliferation of cells in the body can result in tumours and death.
All cancers begin in the cells. Cells send out signals that regulate how much and how frequently they divide. If any of these signals are inaccurate or missing, cells may begin to grow and multiply abnormally, resulting in a lump known as a tumour. As a result, cancer cells continue to divide indefinitely, developing tumours and damaging your body’s organs.
Types of Cancer
1. Breast Cancer: Breast cancer is a common type of cancer that usually affects women and some other people who were assigned female at birth (AFAB). But did you know that about 1% of men show signs of breast cancer cases that might occur during birth? It starts in the cells of the breast and can be found early with regular check-ups.
2. Lung Cancer: Lung cancer is the second most common cancer. There are two main types: non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. It’s often caused by smoking or being around harmful chemicals. Early diagnosis is important for oncology treatment.
3. Prostate Cancer: This type of cancer affects about 1 in 9 men and some people are assigned male at birth (AMAB). It starts in the prostate gland, which is a small organ below the bladder.
4. Colorectal Cancer: Colon cancer and rectal cancer are types of colorectal cancer. They affect different parts of your digestive system. Eating healthy and getting screened can help prevent these cancers.
5. Blood Cancers: Leukemia and lymphoma are common blood cancers. They affect the cells that help your body fight infections. Treatments like chemotherapy and bone marrow transplants can help fight these cancers.
Symptoms of Cancer
The hardest part about cancer is how difficult it is to detect. When a person notices symptoms of cancer, the damage is already done. Cancer has almost invariably moved outside of the organ to other parts of the body. Cancer symptoms can vary widely depending on the type and location of the cancer. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
1. Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden, unexplained weight loss of 10 pounds or more can be an early sign of cancer, especially cancers of the pancreas, stomach, oesophagus, or lungs.
2. Fatigue: Extreme tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest can be a symptom of several types of cancer, including leukaemia.
3. Fever: Persistent fevers can be a sign of cancer, often indicating that cancer has spread or affects the immune system, like lymphoma or leukaemia.
4. Pain: Persistent pain, such as back pain, headaches, or bone pain, can be an early symptom of cancer. Bone cancer or testicular cancer often causes pain.
5. Skin Changes: Changes in the skin such as new growths, sores that don’t heal, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and changes in existing moles can indicate skin cancer or other types.
6. Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits: Long-term constipation, diarrhea, changes in stool size, or blood in the stool can be symptoms of colon cancer. Bladder cancer might present as blood in the urine or frequent urination. It is important to seek medical advice for appropriate diarrhea treatment if symptoms persist.
7. Persistent Cough or Hoarseness: A persistent cough or a change in voice might indicate lung cancer or cancer of the larynx.
8. Unusual Bleeding or Discharge: Unexplained bleeding can occur in early or advanced cancer. Blood in the urine might be a sign of bladder or kidney cancer; blood in the stool could indicate colorectal cancer.
9. Lumps or Thickening: New lumps or thickening in the breast, testicles, or other body parts might indicate cancer.
10. Difficulty Swallowing: Persistent difficulty in swallowing could be a symptom of oesophagal or throat cancer.
11. Indigestion or Difficulty Eating: Constant indigestion or discomfort after eating can be a sign of stomach or oesophagal cancer.
Causes of Cancer
It’s crucial to understand the causes of cancer because it’s not a single disease. The term “cancer” refers to a group of diseases with one thing in common: uncontrolled cell multiplication. Several factors can be cause of cancer:
- Viruses include human papillomavirus, hepatitis B virus, and herpes virus-8.
- Toxins or irritants in the environment. Exposure to Asbestos, benzene, benzidine, cadmium, nickel, arsenic, radon, and vinyl chloride has been linked to cancer in numerous studies.
- Damage to a cell’s DNA causes some cancers. Heat or light from the sun, microwaves from an oven, X rays from an X-ray tube, and gamma rays from radioactive elements can ionize and alter cell DNA.
Early Detection of Cancer
The greatest method to combat cancer is to detect it early. For example, when breast cancer is detected early through a particular check-up known as screening, there is a greater chance of curing it. New technology allows doctors to detect cancer sooner and more accurately than ever. There are several approaches you can take to detect cancer when it is tiny and easier to treat. The sooner cancer is detected, the more therapy options are available. Here are some techniques to detect cancer early.
Early detection of cancer does not guarantee a cure, but it raises the likelihood that present treatments will result in a cure. Early detection also increases the likelihood that the patient would have a far less painful treatment experience than they would otherwise.
Get Checked for Common Types of Cancer: The best method to detect cancer early is to get tested for the types that occur most frequently where you live. These check-ups can find cancer when it’s just starting, which helps people get treated before it gets worse.
Remember, doctors are working hard to find better ways to find and treat cancer early. Taking care of yourself and getting regular check-ups can help keep you healthy
Is Cancer Genetic?
Cancer is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by alterations in genes that control how our cells behave, mainly how they grow and divide.
Inherited characteristics play a role in the development of several cancers. You can inherit mutations in your genes from your parents, increasing your risk of developing cancer.
Some cancers that can be hereditary are:
- Breast cancer.
- Colon cancer.
- Prostate cancer.
- Ovarian cancer.
- Uterine cancer.
- Melanoma (a type of skin cancer)
- Pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Risk Factors
The annual cancer incidence rate is 442.4 per 100,000 men and women. Based on 2013-2017 deaths, the cancer mortality rate is 158.3 per 100,000 men and women annually.
By 2040, the annual number of new cancer cases is predicted to reach 29.5 million, with 16.4 million cancer-related deaths.
Generally, cancer risk factors include:
- Older age
- Family history of cancer
- Alcohol/Tobacco consumption
- Viral infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Exposure to specific chemicals such as Asbestos, nickel, cadmium, radon, vinyl chloride, benzidine, and benzene
- High-energy radiation, including ultraviolet radiation from the sun, can damage DNA and cause cancer.
How can I reduce my risk of developing cancer?
- Avoid Tobacco
- Eat a Healthy Diet
- Stay Physically Active
- Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Protect Yourself from the Sun
- Minimize Exposure to Carcinogens
Common Types of Treatment for Cancer
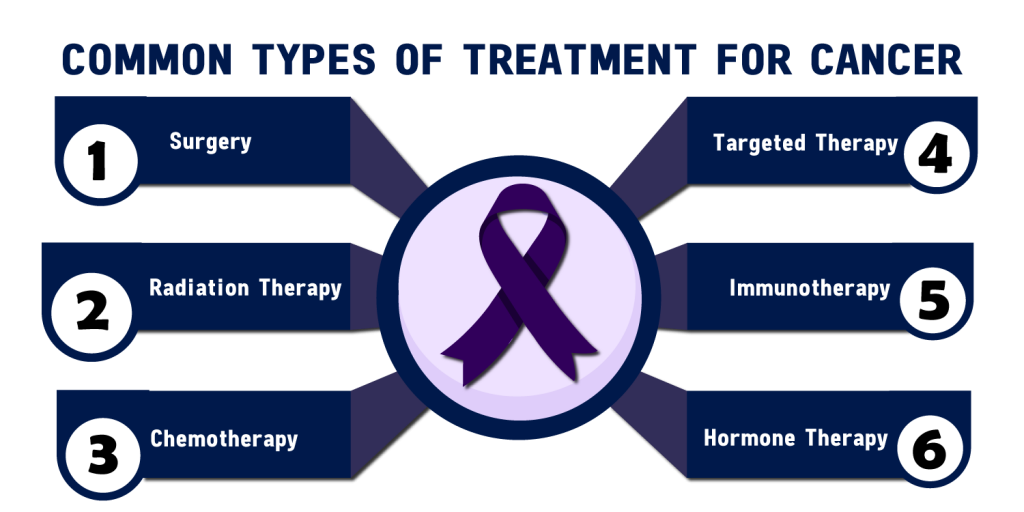
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Targeted Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Stem Cell or Bone Marrow Transplant
- Hormone Therapy
Cancer Treatment
Numerous methods and medications are available to treat cancer, with many more under investigation. Some therapies are “local,” such as surgery and radiation therapy, and are used to treat a specific tumour or body part. Because drug treatments (such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy) can influence the entire body, they are commonly referred to as “systemic” treatments. Moreover, doctors also demand Blood tests for Cancer treatment.
Preventing Cancer
Cancer prevention is simply about making good lifestyle choices and taking good care of your overall health.
- Avoid Tobacco and Alcohol
- Keep body weight controlled and healthy
- Eat lots of fruits and vegetables
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Protect yourself from UV rays exposure
- Limit exposure to outdoor and indoor air pollution, particularly radon.
The Bottomline
Cancer isn’t simply an illness; its emotional impact on family, friends, and everybody else is huge. Patients, relatives, and carers may experience emotional distress as a result of a cancer diagnosis. Many cancers are asymptomatic in their early stages, which is why regular screenings are so important. It’s critical to notice minor changes and seek help when necessary. At Kayawell, we connect you with the top Oncologists who can explain cancer symptoms, dangers, and prevention in depth. Feel free to contact these professionals if you or someone you know has cancer questions. Find top experts nearby easily here.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.