Albumin: Because of the wide range of albumin levels seen in serous body fluids, results are best evaluated by using the serum albumin ascites gradient. A gradient greater than 1.1 g/dL predicts portal hypertension with 97-98% accuracy and is seen in transudates. A gradient less than or equal to 1.1 g/dL is usually seen with exudates.
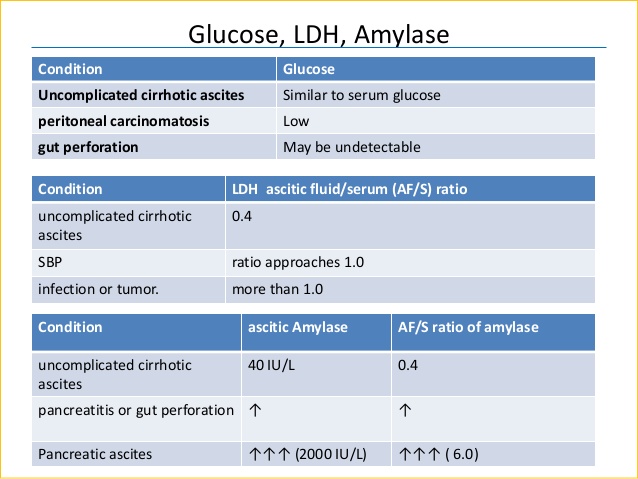
Amylase: Values greater than or equal to three times (3x) a simultaneously analyzed serum value, are considered abnormal in ascites of pancreatic origin. Other peritoneal and intestinal disorders may also cause elevation of amylase.
Bilirubin, Total: An ascetic fluid bilirubin levels have been examined in patients with various forms of ascites. An ascetic fluid bilirubin concentration greater than 6 mg/dL and an ascitic fluid to serum bilirubin ratio of greater than 1.0 appears to be consistent with bile peritonitis.
CA 19-9: Less than 35 U/mL. This test was performed using the Siemens Centaur, Chemiluminescent method.Values obtained with different assay methods or kits cannot be used interchangeably. This test should not be interpreted as absolute evidence for the presence or absence of malignant disease.
Cholesterol: Less than 48 mg/dL.
Creatinine: 0.5 – 2.0 mg/dL.
Glucose: Reference range approximates that found in serum.
LD (Lactate Dehydrogenase): Less than 63 U/L.
Protein, Total:
Transudates: Less than 3.0 g/dL.
Exudates: Greater than or equal to 3.0 g/dL.
Triglycerides: Less than 65 mg/dL.


 Contact Us
Contact Us






 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog
























Comments